The technology isn't the bottleneck. A junior analyst can generate a Python script in seconds, but your enterprise architecture review takes three weeks.
The real challenge in enterprise AI adoption is organizational, not technical. It's about transforming how people work, not just what tools they use. And that's where most initiatives quietly fail—not in a spectacular explosion of bad technology, but in the slow fade of declining usage after the initial rollout excitement wears off.
The data tells a clear story: 91% of middle-market executives report using AI in some capacity, with 88% planning to increase budgets (RSM, 2025). Yet fewer than 25% consistently capture ROI at scale from their efforts (McKinsey, 2024). The gap between adoption and value realization isn't a technology problem—it's a strategy, enablement, and culture problem.
This playbook addresses that gap. It's for AI program leaders, internal champions, and business unit leaders who need to drive adoption that actually sticks—not the kind that shows impressive numbers in the first month, then quietly dies when the executive dashboard stops tracking it.
Why Most AI Initiatives Fail
The primary cause of AI project failure isn't model performance or integration complexity. It's the absence of clear objectives. Organizations treat GenAI as a technology experiment rather than a strategic initiative aligned with business outcomes.
Three patterns emerge in failed adoptions:
Pattern 1: The Pilot Graveyard Projects launch with enthusiasm, generate interest, then stall when nobody can articulate what success looks like. Without clear business objectives and success metrics, even technically sound implementations become organizational orphans.
Pattern 2: Shadow AI Chaos IT bans unapproved tools. Employees continue using them anyway—on personal accounts, with company data, creating compliance landmines nobody knows about until it's too late. You can't block your way to adoption; you have to outcompete the alternatives.
Pattern 3: Training Theater The organization runs a two-hour training session, declares victory, and wonders why usage flatlines at 12% three months later. Sustainable adoption requires behavioral change, not just knowledge transfer.
Organizations with formal AI strategies are nearly twice as likely to experience revenue growth and significantly more likely to report positive ROI—81% versus 64% for informal adoption (Thomson Reuters, 2024). The difference isn't the technology stack—it's the discipline of aligning every initiative to measurable business outcomes.
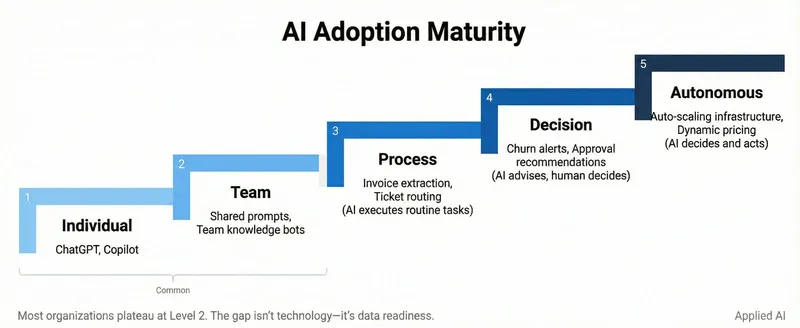
The 5-Level AI Adoption Maturity Model
Successful enterprise AI adoption is incremental, not instantaneous. Attempting to deploy autonomous workflows before your workforce has mastered basic conversational AI is like teaching calculus to people who haven't learned arithmetic.
Level 1: Ad-Hoc & Aware (Conversational Co-pilot)
Individual employees experiment with secure chat interfaces for personal productivity. Usage is decentralized—drafting emails, summarizing documents, brainstorming ideas.
Technology: Enterprise-grade chat (ChatGPT Enterprise, Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini) with SSO and basic DLP policies.
Skills focus: AI literacy for everyone. What GenAI does well, where it hallucinates, and why you shouldn't paste customer data into public tools.
Governance: Initial AI Use Policy defining permissible data (public information, general context) versus off-limits (customer PII, financial data, strategic plans).
Success indicator: When 60%+ of employees can articulate what GenAI is good at and what it hallucinates about, you're ready for Level 2.
Level 2: Systematic & Experimental (Templated Assistants)
Teams move from generic chat to purpose-built AI assistants. Marketing builds a "Brand Voice Assistant" trained on style guidelines. HR creates a "Policy Bot" that knows the employee handbook. Sales develops a "Prospect Research Assistant."
Technology: No-code custom GPT builders (OpenAI GPT Builder, Microsoft Copilot Studio, CustomGPT.ai). Document upload and version control.
Skills focus: Intermediate prompt engineering—crafting system instructions that govern assistant behavior. Use case identification.
Governance: Lightweight review process for publishing custom GPTs. This is where Shadow AI management becomes critical—when the official tool is better than the unsanctioned alternative, people naturally migrate.
Success indicator: Teams building and sharing custom assistants without IT handholding. Shadow AI usage declining.
Level 3: Strategic & Scaled (Connected Intelligence)
AI transitions from static documents to live internal data. Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), assistants query real-time sources—SharePoint, Confluence, CRM systems—providing current, contextually relevant answers.
The Data Readiness Gap: This is where most organizations stall. The jump from Level 2 to Level 3 is deceptively large. You can upload messy PDFs to a Custom GPT and get usable results. Try indexing messy SharePoint content for RAG, and you get hallucinations or irrelevant retrieval. Level 3 requires data quality that Level 2 can tolerate without.
Technology: RAG architectures with vector databases. Enterprise search platforms with semantic understanding (Glean, Microsoft Graph). Role-based access controls.
Skills focus: Data curation at scale. Understanding RAG principles—what's retrievable and what requires different approaches.
Governance: Formal data governance becomes non-negotiable. Classify data by sensitivity. Implement strict access controls. Audit what AI surfaces to whom.
Success indicator: Employees trust AI search more than manual document hunting.
Level 4: Integrated & Automated (Automated Workflows)
AI stops being a conversational endpoint and becomes a step in automated business processes. Support tickets get categorized, routed, with draft responses generated automatically. Sales proposals populate with relevant case studies without human intervention.
Technology: Workflow automation platforms (Zapier, n8n). API connections between LLMs and business systems. Monitoring, alerting, rollback.
Skills focus: Process mapping—deconstructing workflows into automatable steps. API fundamentals. Automation logic with error handling.
Governance: AI Center of Excellence becomes fully operational. MLOps principles—version control, change management, continuous monitoring. Automated workflows need maintenance: models drift, APIs change, business logic evolves.
Success indicator: Multiple departments running automated end-to-end processes with clear monitoring and incident response.
Level 5: Transformative & Agentic (Autonomous Processes)
Instead of predefined workflows, the organization delegates high-level goals to AI agents capable of multi-step reasoning and tool use. "Research top five competitors and produce detailed analysis" triggers an agent that plans tasks, gathers information, synthesizes findings, and delivers a report.
Technology: Agentic AI frameworks (LangChain, custom architectures). Deep API integrations. Sandboxed execution. Real-time human oversight interfaces.
Skills focus: AI strategy at leadership level. Systems thinking. Ethical oversight.
Governance: Advanced ethical review boards. Continuous monitoring for unintended behavior. Robust human-in-the-loop mechanisms that are actually accessible.
Reality check: Current agentic implementations remain experimental. Multi-step agents exhibit compounding reliability issues—a model with 90% accuracy per step yields only 59% accuracy over a 5-step process—requiring heavy guardrails. Most organizations won't need Level 5 for years. The ROI sweet spot lives at Levels 2-4. Don't rush here just because it sounds cutting-edge.
Quick Wins: Building Momentum
The fastest path to sustainable adoption starts with immediate, visible value. Pick the right first projects—not the most impressive, but the highest value for lowest effort and risk.
Ideal characteristics for quick wins:
- Clear input/output requirements
- Existing examples of "good" outcomes
- Repetitive tasks people actually want to eliminate
- Minimal dependencies on other systems
- Fast feedback loops (hours to days, not weeks)
High-Impact Workflows to Start With
| Workflow | Why It Works | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Email drafting | Everyone writes emails; everyone hates routine ones | 30-50% reduction in drafting time |
| Meeting summarization | Universal pain point; clear quality benchmark | 75% reduction in note-taking time |
| Internal knowledge search | Employees waste hours hunting SOPs | 50% reduction in search time |
| Report summarization | Dense documents often skipped | 60-80% reduction in reading time |
| Marketing content drafts | High-volume, formulaic content | 3x faster output |
| First-level support triage | Common questions answered instantly | 30% cost reduction; 80% faster response |
| Sales outreach personalization | Research is valuable but tedious | Higher email response rates |
The pattern: Start with personal productivity wins (Levels 1-2), then scale to team-level automation (Levels 3-4) once the workforce has confidence and competence.
Shadow AI: Managing the Threat
Here's the uncomfortable truth: 78% of your employees are already using unapproved AI tools, and many are inputting sensitive company data (Valence Security, 2024). Banning these tools doesn't stop usage—it drives it underground to personal devices where you have zero visibility.
Shadow AI differs from traditional Shadow IT in one critical way: data entered into public LLMs may be used for training and can never be fully retracted. Once source code, customer emails, or strategic plans enter an external model, that information is potentially permanent.
The Four-Step Mitigation Strategy
1. Discover: Use SaaS management platforms and network signals (DNS logs for `api.openai.com`, browser extension audits, CASB anomalies) to see which AI applications employees actually use. This isn't surveillance—it's understanding unmet needs. If everyone's using a specific tool, that's a clear signal regarding gaps in your sanctioned stack. Shadow AI is your best source of requirements gathering—if 50 people are using an unsanctioned PDF parser, build a better PDF parser.
2. Educate: Launch targeted communication explaining specific risks—not "AI is dangerous," but "here's exactly what happens when you paste customer PII into ChatGPT on your personal account, and why that violates GDPR."
3. Enable: Fast-track deployment of enterprise-grade tools that match or exceed public alternatives. When the official tool is more powerful (connected to internal data, trained on company context) and easier to access (SSO, already integrated), employees naturally migrate. Outcompete Shadow AI, don't try to block it.
4. Enforce (Selectively): Implement guardrails, not walls. DLP policies to block transmission of classified data to unapproved domains. But don't block everything—allow experimentation with non-sensitive use cases while protecting critical information.

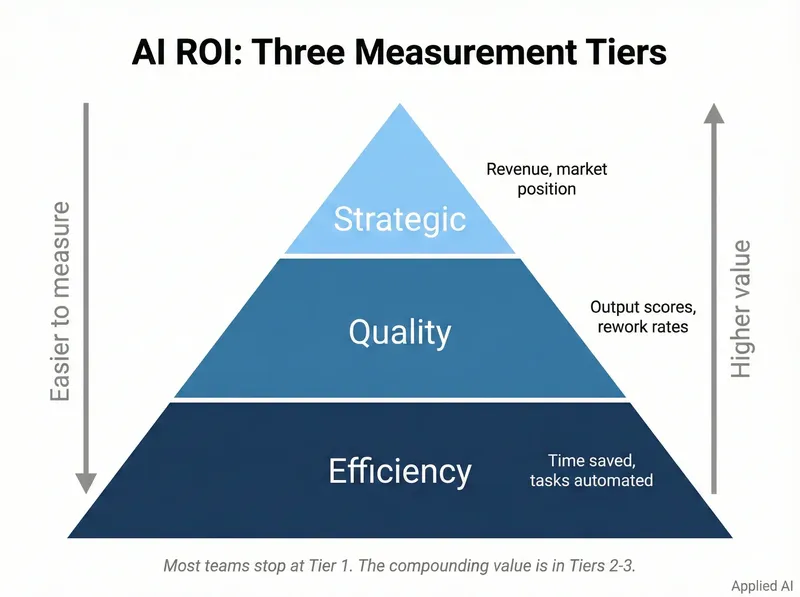
Measuring ROI: A Multi-Layered Framework
Executive support depends on demonstrating tangible business value. Adoption rates and satisfaction scores are useful leading indicators, but they aren't ROI.
Layer 1: Efficiency and Productivity
The most immediate and quantifiable value. Measure time saved and translate to financial impact.
Calculation: (Time saved per task × Tasks automated × Fully-loaded employee cost/hour) – AI solution cost = Efficiency ROI
The Reinvestment Paradox: Be cautious with "time saved" projections. Time saved rarely converts directly to cost savings—it's typically reinvested in higher-quality work. Unless headcount actually decreases or measurable output increases, "efficiency" claims face skepticism from finance.
Examples: Reduced onboarding cycle time (3 days → 4 hours). Automated invoice processing. Marketing team ships 3x more campaigns per quarter.
Layer 2: Revenue Generation
Connecting AI to top-line growth requires careful attribution but demonstrates strategic impact.
Calculation: (New revenue + Incremental revenue) – (AI costs + Program costs) = Revenue ROI
Examples: Improved sales conversion from AI-personalized outreach (14% → 22%). Higher average contract values from AI-assisted proposals ($45K → $63K).
Layer 3: Risk Mitigation
"Value of disaster averted"—cost savings from preventing negative events.
Examples: Reduction in compliance fines through AI-powered policy monitoring. Prevented data breaches via AI security monitoring. Contract risks flagged before signing.
Layer 4: Employee and Customer Experience
Often qualitative, but crucial for sustainable adoption and long-term value.
Track: Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS). Customer Satisfaction (CSAT). Customer churn rate. Employee retention among power users versus non-users.
The Adoption Dashboard
| Category | Metric | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption | Active AI Users % | Breadth of penetration |
| Adoption | Time-to-Proficiency | Training effectiveness |
| Engagement | Prompts per Active User | Depth of daily integration |
| Efficiency | Time Saved per Employee | Core productivity gain |
| Efficiency | Process Cycle Time Reduction | Operational velocity |
| Business Impact | Sales Conversion Rate | Revenue connection |
| Business Impact | CSAT Score | Experience and cost impact |
Connect upstream metrics (adoption, engagement) to downstream outcomes (efficiency, revenue). When you can show that 10% increase in active users correlates with measurable efficiency gains three months later, you've built a business case that survives budget scrutiny.
Change Management: Making New Habits Stick
Technology adoption fails at a 67% rate within 90 days when treated as a one-time training event rather than continuous behavioral change. Sustainable adoption requires deliberate strategies beyond "here's the tool, now use it."
Training: Three Levels
Beginner (All Employees): What GenAI is and how it works (conceptually). Capabilities and limitations including hallucinations. Security protocols—what's safe to input, what's forbidden. Basic prompting framework: Role → Context → Task → Format.
Intermediate (Power Users, Champions): Advanced prompting (Chain-of-Thought, Few-Shot). Building effective custom GPTs. Identifying automation opportunities within team workflows.
Advanced (AI CoE, Technical Teams): RAG system architecture. Workflow automation at scale. Agentic AI principles and governance.
Behavioral Design for Habit Formation
Start with "Why": Every communication articulates direct benefits. Not "AI will transform our company," but "this eliminates the two hours you spend every Friday writing meeting summaries."
Make It Easy: Rich libraries of prompt templates and pre-built custom GPTs. Let people get immediate value without mastering prompt engineering first.
Create Triggers: Integrate AI into established routines. Project kickoff template requires AI-generated summary. Sales process mandates AI-personalized first outreach. The trigger isn't "remember to use AI"—it's "this step in your normal process now includes AI."
Leverage Social Proof: Formal "AI Champions" programs turn enthusiasts into local experts who run demos, answer questions, share success stories. Internal Slack channels for sharing prompts and use cases. Monthly highlights of creative AI usage in all-hands meetings.
Incentive Programs That Work
Research shows effective programs reward learning, collaboration, and innovation—not raw usage (Great Place to Work, 2024). Purely usage-based incentives encourage low-quality interactions just to hit targets.
Recognition-Based: "AI Champion of the Month" awards. Features on company intranet highlighting creative applications.
Opportunity-Based: Innovation challenges where teams submit AI solution ideas. Winners get resources and executive exposure to develop their concept.
Skill-Based: AI training completion as prerequisite for certain promotions. Small bonuses for external certifications.
Getting Started: The First 90 Days
Weeks 1-4: Foundation
- Form cross-functional AI task force with defined roles
- Draft initial AI Use Policy
- Select enterprise-grade chat interface
- Launch mandatory AI literacy training
Weeks 5-8: Quick Wins
- Identify 3-5 "low-hanging fruit" workflows
- Deploy solutions with clear before/after metrics
- Recruit 10-15 AI Champions from early adopters
- Establish internal communication channel
Weeks 9-12: Momentum
- Publish first ROI metrics showing efficiency gains
- Deploy intermediate training focused on prompt engineering for power users
- Pilot first custom GPTs built by business teams (not IT)
- Conduct Shadow AI discovery
- Plan Level 2 rollout based on learnings
Success at 90 days: 60%+ active monthly users, 3+ documented quick wins with quantified impact, AI Champions program operational, Shadow AI migration plan in place.
That's the foundation. Everything else builds from there.
References
Great Place to Work (2024). "How the 100 Best Companies Are Training Their Workforce for AI."
McKinsey (2024). "The State of AI: How Organizations Are Rewiring to Capture Value."
Microsoft (2024). "3 Proven Ways to Boost AI Usage and Make It Stick." Microsoft WorkLab.
OpenAI Academy (2024). "Planning Your ChatGPT Rollout."
RSM US (2025). "AI for CXOs: Achieving Enterprise AI Adoption."
Thomson Reuters (2024). "Beyond Adoption: How Professional Services Can Measure Real ROI from GenAI."
Valence Security (2024). "AI Security: Shadow AI is the New Shadow IT."
Further Reading
- Enterprise AI Strategy — Strategic framework for AI transformation
- LLM Application Lifecycle — Production patterns for LLMOps
This playbook synthesizes research from industry reports (McKinsey, Deloitte, Thomson Reuters), enterprise AI implementations, and controlled studies (BCG/Harvard) demonstrating 25-40% productivity gains from structured GenAI adoption.
